ปรึกษาหมอกัณฒิภัสส์
?ความดันโลหิตสูงคืออะไร?
ความดันโลหิต คือ แรงดันของเลือดที่กระทำต่อผนังหลอดเลือดแดงขณะที่หัวใจบีบตัวและคลายตัว เราจะวัดค่าความดันโลหิตออกมาเป็นตัวเลข 2 ค่า คือ:
? ค่าความดันตัวบน (Systolic Blood Pressure): คือแรงดันสูงสุดขณะที่หัวใจบีบตัว
? ค่าความดันตัวล่าง (Diastolic Blood Pressure): คือแรงดันต่ำสุดขณะที่หัวใจคลายตัว
?เมื่อไหร่ที่เรียกว่าความดันโลหิตสูง? โดยทั่วไปสำหรับประชาชน ค่าความดันโลหิตที่ถือว่า “ปกติ” คือ น้อยกว่า 120/80 มิลลิเมตรปรอท (มม.ปรอท) หากวัดค่าความดันโลหิตได้ 140/90 มม.ปรอท หรือสูงกว่า ถือว่าเข้าข่ายเป็นโรคความดันโลหิตสูงแล้ว (ยกเว้นในกลุ่มคนที่มีโรคประจำตัวบางอย่างที่แพทย์อาจกำหนดค่าเป้าหมายที่ต่ำกว่านี้)
❤️สาเหตุหลักที่ทำให้ความดันโลหิตสูงขึ้น:
ส่วนใหญ่มักเกิดจากพฤติกรรมการใช้ชีวิตประจำวัน เช่น
✅ การกินเค็มจัด: อาหารที่มีโซเดียมสูงทำให้ร่างกายกักเก็บน้ำมากขึ้น และเพิ่มปริมาณเลือดในหลอดเลือด
✅ความเครียด: ทำให้ร่างกายหลั่งฮอร์โมนที่ทำให้หัวใจบีบตัวแรงขึ้นและหลอดเลือดหดตัว
✅การขาดการออกกำลังกายและภาวะอ้วน: ทำให้หัวใจต้องทำงานหนักขึ้น
✅การสูบบุหรี่และดื่มแอลกอฮอล์มากเกินไป
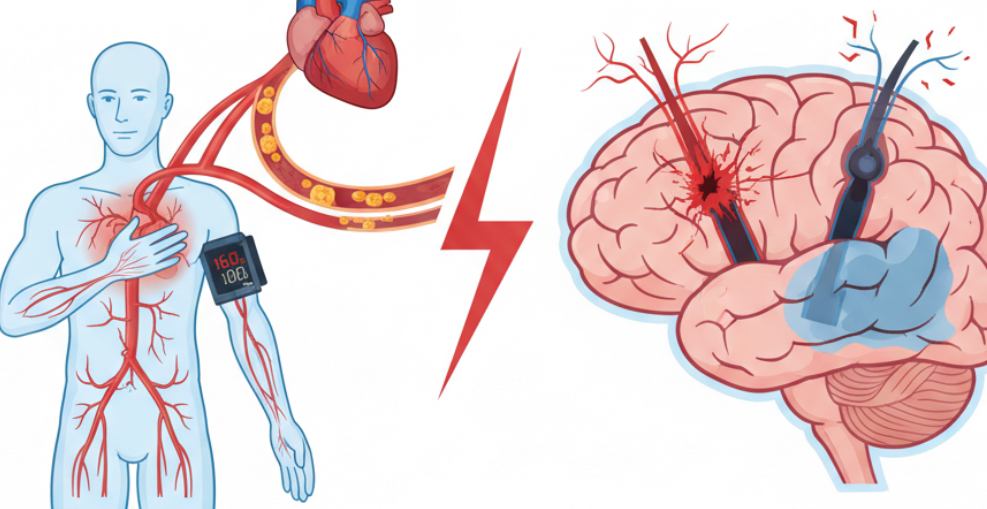
ทำไมความดันโลหิตสูงจึงอันตรายต่อสมอง?
เมื่อความดันโลหิตสูงกว่าปกติอย่างต่อเนื่องเป็นเวลานาน มันจะส่งผลเสียต่อหลอดเลือดทั่วร่างกาย โดยเฉพาะหลอดเลือดแดงที่ไปเลี้ยงสมอง
?กลไกที่นำไปสู่โรคหลอดเลือดสมอง:
- ทำให้หลอดเลือดแข็งและหนาตัว (Atherosclerosis) ความดันที่สูงอย่างต่อเนื่องจะทำลายผนังหลอดเลือด ทำให้เกิดการสะสมของไขมันและคราบตะกรัน ส่งผลให้หลอดเลือดตีบแคบลง (Stenosis) การไหลเวียนของเลือดไปยังสมองจึงลดลง และมีโอกาสเกิดภาวะสมองขาดเลือด (Ischemic Stroke) ซึ่งเป็นชนิดที่พบได้มากที่สุด
- เพิ่มความเสี่ยงหลอดเลือดสมองแตก (Hemorrhagic Stroke): ความดันโลหิตที่สูงมากและควบคุมไม่ได้ จะทำให้หลอดเลือดในสมองรับแรงดันมหาศาล จนผนังหลอดเลือดเปราะบางและแตกออก ทำให้มีเลือดออกในเนื้อสมอง มักมีอาการรุนแรงและอันตรายถึงชีวิต
กล่าวโดยสรุปทางสถิติ, ความดันโลหิตสูงเป็นปัจจัยเสี่ยงหลักของโรคหลอดเลือดสมอง โดยมีรายงานว่าผู้ป่วยโรคหลอดเลือดสมองมากกว่าครึ่งมีภาวะความดันโลหิตสูงร่วมด้วย ดังนั้น การควบคุมความดันโลหิตให้ได้ตามเป้าหมาย จึงเป็นการลดความเสี่ยงโรคหลอดเลือดสมองได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ
?สังเกตและป้องกัน: เราจะทำอะไรได้บ้าง?
เนื่องจากความดันโลหิตสูงไม่มีอาการเตือน การเฝ้าระวังจึงสำคัญที่สุด
- การตรวจวัดความดันโลหิต:
ทุกคนควรได้รับการตรวจวัดความดันโลหิตเป็นประจำอย่างน้อยปีละครั้ง หรือวัดเองที่บ้านเป็นระยะ โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งหากมีประวัติครอบครัวเป็นโรคความดันโลหิตสูงหรือมีอายุ 35 ปีขึ้นไป
- การควบคุมและปรับเปลี่ยนพฤติกรรม (หัวใจสำคัญของการป้องกัน):
?การดูแลตนเองคือ “ยาชั้นดี” ที่ป้องกันได้ทั้งความดันโลหิตสูงและโรคหลอดเลือดสมอง:
- ✅ลดเค็ม ลดมัน: จำกัดการบริโภคเกลือและโซเดียม (ไม่ควรเกิน 2,000 มิลลิกรัมต่อวัน หรือเทียบเท่าเกลือ 1 ช้อนชา) หลีกเลี่ยงอาหารแปรรูป อาหารสำเร็จรูป และลดไขมันอิ่มตัว
- ✅เน้นผักและผลไม้: รับประทานผัก ผลไม้ และธัญพืชไม่ขัดสีให้มากขึ้น
- ✅ออกกำลังกายสม่ำเสมอ: ควรออกกำลังกายระดับปานกลาง (เช่น เดินเร็ว, วิ่งเหยาะๆ) อย่างน้อย 30 นาทีต่อวัน 5 วันต่อสัปดาห์
- ✅ควบคุมน้ำหนัก: รักษาน้ำหนักตัวให้อยู่ในเกณฑ์มาตรฐาน (ดัชนีมวลกาย หรือ BMI ไม่ควรเกิน 25)
- ✅งดเหล้า เลิกบุหรี่: การสูบบุหรี่และดื่มแอลกอฮอล์ทำลายหลอดเลือดโดยตรงและเพิ่มความดันโลหิต
- สัญญาณเตือนโรคหลอดเลือดสมอง: จำให้ขึ้นใจ!
หากมีอาการเหล่านี้แม้เพียงเล็กน้อย ควรรีบไปโรงพยาบาลทันที
Face (หน้า): ใบหน้าอ่อนแรง หรือปากเบี้ยว
Arms (แขน): แขนขาอ่อนแรงข้างใดข้างหนึ่ง หรือชาครึ่งซีก
Speech (พูด): พูดไม่ชัด พูดติดขัด หรือนึกคำพูดไม่ออก
Time (เวลา): ให้รีบไปโรงพยาบาลทันที! โทร 1669
การป้องกันคือการลงทุนที่คุ้มค่าที่สุดนะครับ
แผนที่ google map ครับ เปิด GPS จีพีเอส คลิกเลย
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
What is high blood pressure?
Blood pressure is the force of blood against the artery walls as the heart contracts and relaxes. Blood pressure is measured in two numbers:
? Systolic Blood Pressure: The highest pressure when the heart contracts.
? Diastolic Blood Pressure: The lowest pressure when the heart relaxes.
?When is high blood pressure considered high? Generally, for the general public, a blood pressure reading of 140/90 mmHg or higher is considered high blood pressure (except for those with certain underlying medical conditions, for which a doctor may set a lower target).
❤️ Main causes of high blood pressure:
It is usually caused by lifestyle habits, such as:
✅ Eating too much salt: Foods high in sodium cause the body to retain more water and increase blood volume in the blood vessels.
✅ Stress: Causes the body to release hormones that increase the heart’s contraction and constrict blood vessels.
✅ Lack of exercise and obesity: Makes the heart work harder.
✅ Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Why is high blood pressure dangerous to the brain?
When blood pressure is consistently higher than normal for a long period of time, it negatively impacts blood vessels throughout the body, especially the arteries that supply the brain.
? Mechanisms leading to stroke:
Atherosclerosis (hardening and thickening of the arteries). Chronically high blood pressure damages blood vessel walls, causing the buildup of fat and plaque. This narrows blood vessels (stenosis). This reduces blood flow to the brain, increasing the risk of ischemic stroke, the most common type.
Increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke: Extremely high and uncontrolled blood pressure puts enormous pressure on blood vessels in the brain, causing the vessel walls to become fragile and rupture, leading to bleeding into the brain tissue. This often leads to severe and life-threatening symptoms.
Statistically, high blood pressure is the main risk factor for stroke. It’s reported that more than half of stroke patients also have high blood pressure. Therefore, achieving targeted blood pressure control effectively reduces the risk of stroke.
? Observation and Prevention: What can we do?
Since high blood pressure has no warning symptoms, Monitoring is therefore paramount.
Blood Pressure Monitoring:
Everyone should have their blood pressure measured regularly, at least annually, or at home periodically, especially if they have a family history of high blood pressure or are over 35 years of age.
Behavioral Control and Modification (Key to Prevention):
?Self-care is the “best medicine” that can prevent both high blood pressure and stroke:
✅ Reduce Salt and Fat: Limit salt and sodium intake (no more than 2,000 milligrams per day, or the equivalent of 1 teaspoon of salt). Avoid processed foods and ready-to-eat foods, and reduce saturated fat.
✅ Focus on Fruits and Vegetables: Eat more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
✅ Regular Exercise: Moderate exercise (such as brisk walking or jogging) for at least 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week.
✅ Weight Control: Maintain a healthy weight (BMI should not exceed 25).
✅ Quit Alcohol and Smoking: Smoking and drinking alcohol directly damage blood vessels and increase blood pressure.
Stroke Warning Signs: Remember these!
If you experience even mild symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Face: Facial weakness. Or a crooked mouth.
Arms: Weakness or numbness on one side of the arm or leg.
Speech: Slurred speech, stuttering, or difficulty forming words.
Time: Seek immediate medical attention! Call 1669.
Prevention is the best investment.