?อาการแน่นหน้าอก เป็นอาการที่ไม่มีใครอยากเจอ เพราะมักจะมาพร้อมกับความกังวลว่า “กำลังเป็นโรคหัวใจอยู่หรือเปล่า?” ความจริงแล้ว อาการแน่นหน้าอกนั้นเป็นเหมือนสัญญาณเตือนที่ร่างกายส่งออกมาจากหลายอวัยวะ ไม่ได้จำกัดอยู่แค่ที่หัวใจเท่านั้น แต่ยังรวมถึง ปอด, ระบบย่อยอาหาร, กล้ามเนื้อ และแม้แต่ ความเครียด ก็สามารถทำให้คุณรู้สึกแน่นหน้าอกได้
✌️หมอแนะ สิ่งสำคัญทั่วไปคือการสังเกตและแยกแยะความแตกต่างของอาการ เพื่อตัดสินใจได้ถูกว่าอาการที่เป็นอยู่นั้นเสี่ยงอันตรายถึงชีวิตหรือไม่นะครับ
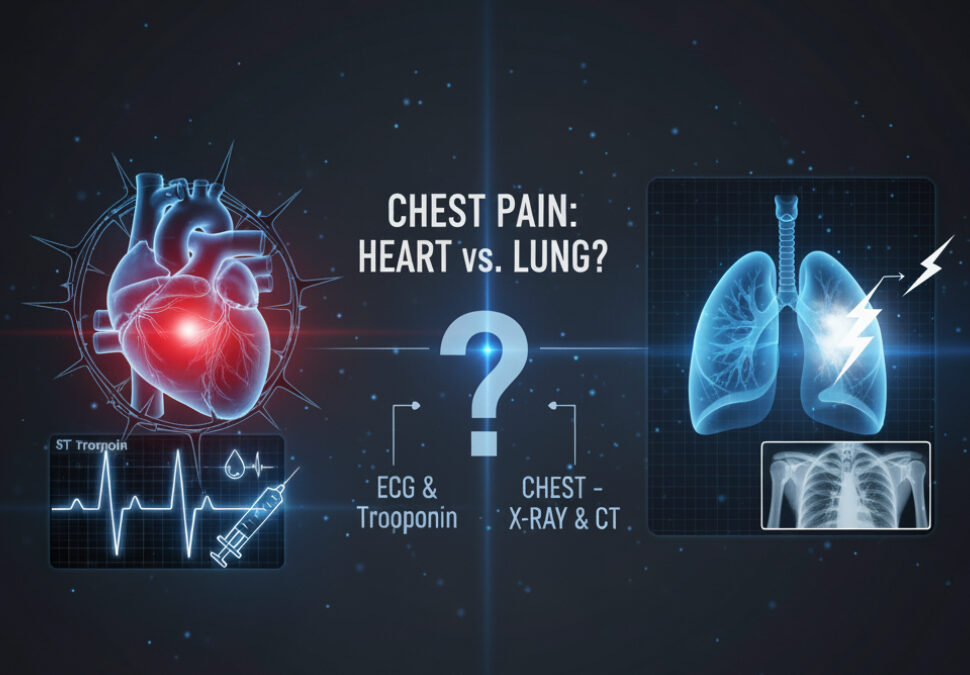
แยกอาการแน่นอก: “สัญญาณอันตราย” จากหัวใจและปอด
?อาการแน่นหน้าอกที่เกิดจากหัวใจและปอดนั้นเป็นสิ่งที่อันตรายและควรได้รับการรักษาอย่างเร่งด่วน การสังเกตลักษณะอาการอย่างละเอียดจะช่วยให้ประเมินความเสี่ยงได้เบื้องต้นได้ครับ
| ลักษณะอาการ | หากเป็น “หัวใจ” (เช่น กล้ามเนื้อหัวใจขาดเลือด) | หากเป็น “ปอด” (เช่น เยื่อหุ้มปอดอักเสบ) |
| ตำแหน่งและความรู้สึก | รู้สึกแน่น จุก หรือหนักคล้ายมีอะไรมาทับ กลางหน้าอก | มักเป็นความเจ็บปวดแบบ เจ็บแปลบ หรือ เจ็บแหลม มักอยู่บริเวณ ด้านข้าง หรือตำแหน่งใดตำแหน่งหนึ่งชัดเจน |
| การปวดร้าว | มักมีอาการร้าวไปที่ แขนซ้าย (หรือทั้งสองข้าง) คอ กราม หรือ หลัง | การปวดมักจะจำกัดอยู่ที่บริเวณหน้าอก ไม่ร้าวไปที่อื่น (ยกเว้นบางโรค เช่น ลิ่มเลือดอุดตันในปอด) |
| ความสัมพันธ์กับการออกแรง | มักเกิดอาการเมื่อ ออกแรง ออกกำลังกาย หรือมี อารมณ์เครียดจัด และจะ ดีขึ้นเมื่อได้พัก | มักจะไม่สัมพันธ์กับการออกแรง แต่จะ เจ็บมากขึ้นเมื่อหายใจเข้าลึก ๆ ไอ หรือจาม |
| อาการอื่น ๆ ร่วม | เหงื่อแตก ตัวเย็น คลื่นไส้ หายใจลำบาก หรือ ใจสั่น | ไอเรื้อรัง มีเสมหะ หายใจมีเสียงวี๊ด หรือมีไข้ (ในกรณีของปอดอักเสบ) |
อาการแน่นอกที่เกิดจากสาเหตุอื่น ๆ ได้อีกนะครับ
?ไม่ใช่ทุกอาการแน่นหน้าอกจะอันตรายถึงชีวิต และบางครั้งอาการเหล่านี้ก็ถูกเข้าใจผิดว่าเป็นโรคหัวใจได้บ่อย:
- จากระบบทางเดินอาหาร: กรดไหลย้อน (GERD) มักทำให้เกิดอาการ แสบร้อนบริเวณหน้าอก ร้าวขึ้นคอหรือลิ้นปี่ อาการมักเป็นหลังมื้ออาหาร โดยเฉพาะมื้อใหญ่ หรือเมื่อเอนตัวลงนอน
- จากกล้ามเนื้อและกระดูก: เกิดจากกล้ามเนื้ออักเสบ หรือการอักเสบของกระดูกอ่อนซี่โครง (Costochondritis) มักมีอาการเจ็บที่จุดใดจุดหนึ่งชัดเจน และ เจ็บมากขึ้นเมื่อกดบริเวณนั้น หรือเมื่อมีการเคลื่อนไหวของลำตัว
- จากความเครียด/วิตกกังวล: อาการแพนิก (Panic Attack) สามารถทำให้เกิดอาการแน่นหน้าอก หายใจหอบถี่ ใจสั่นมาก และรู้สึกเหมือนจะขาดใจ แต่เมื่ออาการสงบลง อาการแน่นหน้าอกก็จะหายไป
❤️การแยกสาเหตุของอาการแน่นหน้าอกจำเป็นต้องใช้เครื่องมือช่วยวินิจฉัย เช่น การตรวจคลื่นไฟฟ้าหัวใจ (EKG/ECG), การตรวจระดับเอนไซม์ Troponin ในเลือด (บ่งชี้ความเสียหายของกล้ามเนื้อหัวใจ), และ การเอกซเรย์ทรวงอก (Chest X-ray) หรือ CT Scan เพื่อประเมินภาวะลิ่มเลือดอุดตันในปอดหรือโรคปอดอื่น ๆ
#พัทยา 2 คลินิกเฉพาะทางอายุรกรรม #ตรวจคลื่นไฟฟ้าหัวใจ EKG #เอกเร์ปอด chest x-ray #ตรวจเลือด เอนไซหัวใจ blood test Troponin I high sense
โทร 0833309366
เปิดทุกวัน
จันทร์ ถึง พุธ 16.30 – 20.00 น.
พฤหัส ถึง ศุกร์. 8.00 – 20.00 น.
วันเสาร์ 8.00 – 12.00 น.
อาทิตย์ 8.00 – 16.00 น.
Monday – Wednesday 4.30 pm to 8 pm
Thursday – Friday 8 am to 8 pm
Saturday 8 am to noon
Sunday 8 am to 4 pm
แผนที่ google map กดที่ลิ้ง http ได้เลยครับ
https://maps.app.goo.gl/8q59d
++++++++++++++++++++++++++
? Chest tightness is a symptom no one wants to experience. It’s often accompanied by the worry, “Do you have heart disease?” In fact, chest tightness is a warning sign sent from multiple organs. It’s not limited to the heart, but also includes the lungs, digestive system, muscles, and even stress.
✌️ Doctors recommend observing and distinguishing symptoms is essential to properly determine whether your condition is life-threatening.
Distinguishing Chest Tightness: “Danger Signs” from the Heart and Lungs
? Chest tightness caused by the heart and lungs is dangerous and requires immediate treatment. Careful observation of the symptoms can help assess your risk.
Symptoms: If it’s “heart” (e.g., ischemic heart disease) or “lung” (e.g., pleurisy),
Location and sensation: A feeling of tightness, aching, or a feeling of pressure in the center of the chest. This pain is often sharp or sharp, typically located on the side or in one specific location.
Radiating pain often radiates to the left arm (or both arms), neck, jaw, or back. The pain is usually confined to the chest. It does not radiate to other areas (except for certain conditions, such as a pulmonary embolism).
Exercise-related: Symptoms usually occur with exertion, exercise, or extreme stress, and improve with rest. It is usually not related to exertion, but the pain worsens with deep breathing, coughing, or sneezing.
Other symptoms include sweating, a cold body, nausea, difficulty breathing, or palpitations, a chronic cough, phlegm production, wheezing, or fever (in the case of pneumonia).
Chest tightness can also be caused by other causes.
?Not all chest tightness is life-threatening, and these symptoms are often mistaken for heart disease:
Gastrointestinal: Acid reflux (GERD) often causes a burning sensation in the chest, radiating up the throat or epigastrium. Symptoms often occur after meals, especially large meals, or when lying down.
Musculoskeletal: Caused by muscle inflammation or costochondritis. Pain is often localized in a specific area and worsens with pressure or body movement.
Stress/Anxiety: Panic attacks can cause chest tightness, shortness of breath, severe palpitations, and a feeling of suffocation. However, once the symptoms subside, the tightness disappears.
❤️To distinguish the cause of chest tightness, diagnostic tools such as an electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG), a blood troponin test (indicating heart muscle damage), and a chest X-ray or CT scan to evaluate for pulmonary embolism or other lung diseases.